Energy, an essential commodity for economic stability and growth, is mostly supplied within a centralized and vertically integrated power market. Conventional power market structures, as we know them, involve power generation, transmission, and distribution through the existing energy grid to customers facing an inelastic supply market.
As the need for more adaptive and responsive energy systems grows, the energy landscape is shifting towards a more decentralized and dynamic framework. Tomorrow’s power market is defined by a bi-directional distributed supply with intermittent prices. It features a decentralized power generation approach, incorporating a diverse range of sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and other distributed energy resources. A horizontal network of mobility and communication infrastructure ensures more integrity, creating a power grid capable of coordinating markets with a rising amount of technical complexity and transactions. This power grid creates the foundation for the Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) concept, a system that will replace the traditional centralized model.
EaaS is a business model that provides energy solutions to customers as a service, shifting the traditional ownership and management of energy infrastructure to third-party providers. This approach allows consumers to access and utilize energy services without the need to own or maintain the underlying equipment, promoting efficiency, flexibility, and often incorporating renewable energy sources.
Navigant estimates that the EaaS market could more than double from 2020 to 2026, growing from USD 100 billion to over USD 220 billion. Examples of EaaS include Solar-Energy-as-a-Service (SEaaS), Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), peer-to-peer energy trading, and Virtual Power Plants (VPP).
Solar-Energy-as-a-Service
Diving into SEaaS, let's explore Solar-Energy-as-a-Service in detail. Unlike conventional photovoltaic setups requiring a substantial upfront investment, SEaaS offers a subscription-based alternative. Through this model, solar energy plants are made available to customers without the need for them to purchase or possess PV installations. The subscription essentially functions as a long-term power purchase agreement (PPA) between households or companies and energy service providers. Importantly, these subscriptions typically cover not only the installation but also the ongoing operation and maintenance of the solar energy plant, further reducing the burden on the customers.
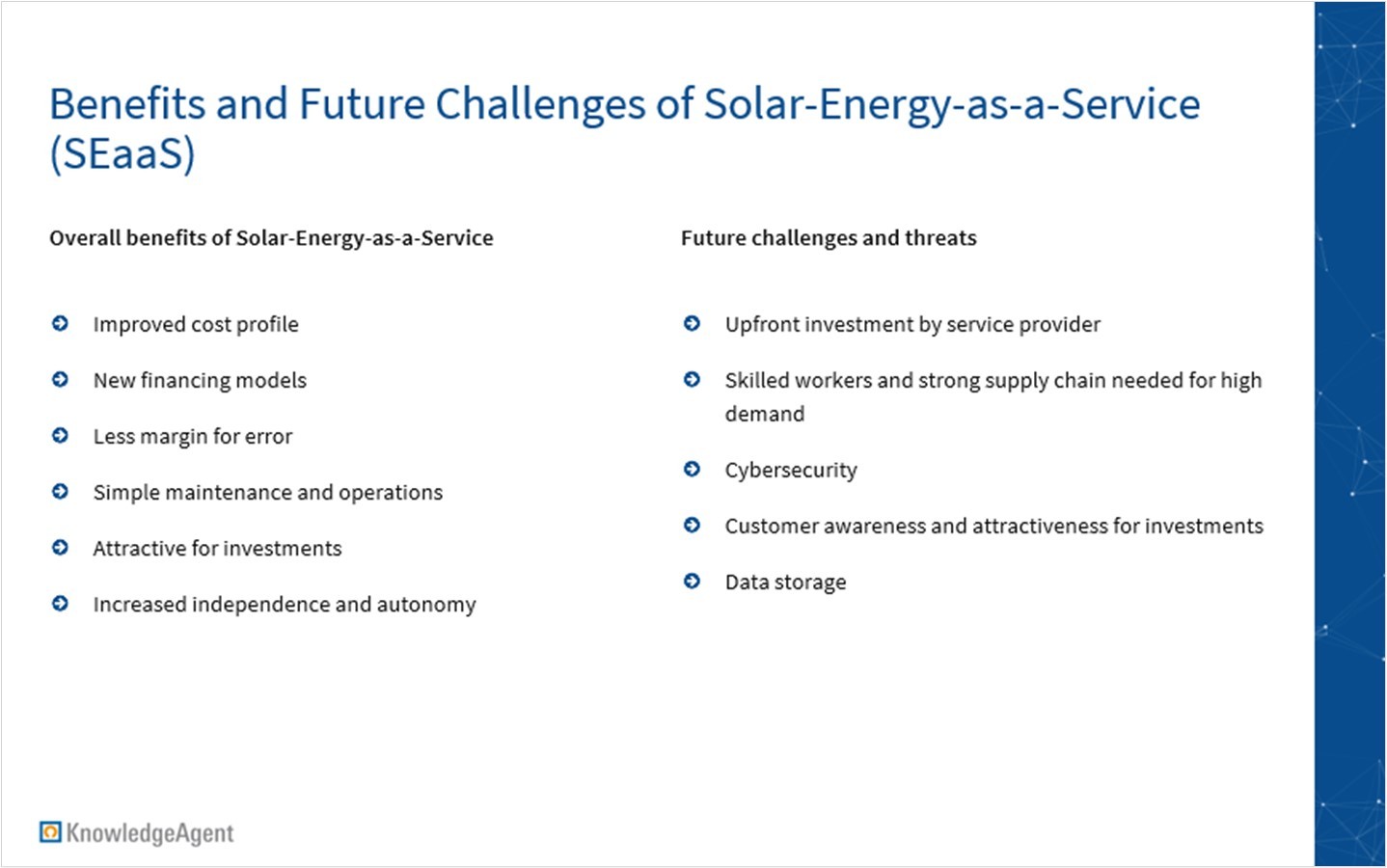
Additionally, SEaaS fosters grid resilience by promoting distributed energy sources, reducing reliance on centralized power systems, and contributing to a more robust and sustainable energy future. The market, however, faces challenges in grid integration complexity and competition with entrenched traditional energy models. The necessity of a strong and reliable supply chain, along with qualified installation partners, adds to the complexities.
Incentives for private investment into Solar-Energy-as-a-Service
The SEaaS market is poised for growth, supported by regulatory incentives such as the EU's solar energy strategy. The REPowerEU plan, aiming to add 320 GW of solar photovoltaic capacity by 2025, aligns with the European Commission's action plan, emphasizing incentives for PV installations. Efficient implementation of SEaaS is vital for achieving these ambitious goals.
Examining the German market reveals leading Energy Service Provider Companies (ESPCs) such as Sonnen GmbH, Lichtblick, Enpal, 1Komma5, and Zolar, which have successfully implemented SEaaS offerings, showcasing its viability and scalability.
Future potential
The potential of SEaaS extends far beyond its current applications. As technology continues to advance, SEaaS stands at the forefront of ushering in a new era of energy accessibility and sustainability. The scalability and adaptability of SEaaS make it a cornerstone in addressing the growing global demand for clean energy solutions. With innovations such as advanced energy storage systems and smart grid technologies, SEaaS has the potential to enhance its efficiency, further reducing costs and increasing the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix. The decentralized nature of SEaaS not only empowers individual consumers but also contributes significantly to building resilient, eco-friendly communities.
Change in the energy grid
The transition to a fully integrated Energy-as-a-Service power market necessitates adaptations in the energy grid. Operational changes are essential for enabling new business models to thrive. SEaaS, with its network of solar installations, enhances grid resilience, reduces transmission losses, minimizes dependence on centralized sources, and contributes to a more adaptive and sustainable energy infrastructure.
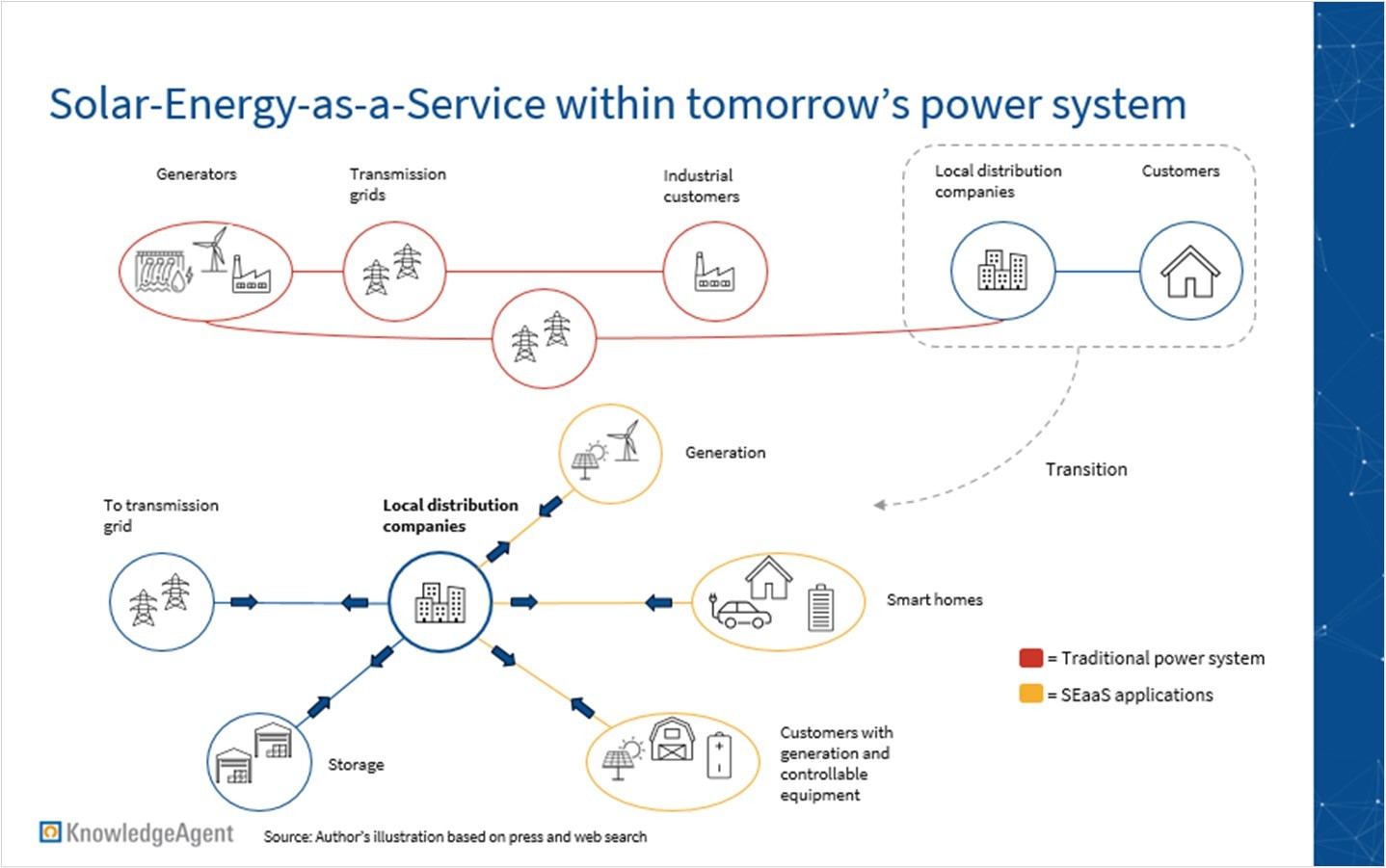
In conclusion, the transformative potential of SEaaS, particularly in reshaping the energy landscape, is evident. As challenges are met and regulatory support accelerates market growth, SEaaS emerges as a pivotal force in driving sustainable energy practices and shaping the future of energy consumption.
About KnowledgeAgent
At KnowledgeAgent, we provide market insights on renewable energies to help stakeholders navigate this evolving landscape. Our team gathers data on ESPCs within the energy supply market and keeps an eye on emerging trends such as Solar Energy-as-a-Service (SEaaS). Reach out to us to stay up to date on the dynamic energy supply landscape, evolving Energy-as-a-Service offerings, and their effects on adjacent energy solution markets.
Sources:
-
International Energy Agency (IEA), Renewables 2022: Executive Summary, https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2022/executive-summary, accessed 17/01/2024
-
Ornate Solar, The Top 5 Solar Countries in the World (2023), https://ornatesolar.com/blog/the-top-5-solar-countries-in-the-world, accessed 17/01/2024
-
European Commission – European Energy Efficiency Platform (E3P), Energy Service Companies (ESCos), https://e3p.jrc.ec.europa.eu/node/190, accessed 17/01/2024
-
Deloitte, Energy-as-a-Service The lights are on. Is anyone home?, https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/uk/Documents/energy-resources/deloitte-uk-energy-as-a-service-report-2019.pdf, accessed 17/01/2024
-
Solnet, Solutions: Solar Energy as a Service, https://www.solnet.group/solar-energy-as-a-service, accessed 17/01/2024
-
InnoEnergy, Renewable Energies: Solar-as-a-Service, https://www.innoenergy.com/discover-innovative-solutions/online-marketplace-for-energy-innovations/solar-as-a-service/, accessed 17/01/2024
-
PlicoEnergy, How Solar As A Service (SAAS) Will Bring Solar Systems With Battery Storage To Every Australian At A Net Neutral Weekly Cost, https://www.plicoenergy.com.au/article-solar-as-a-service, accessed 17/01/2024
-
TrinaSolar, Why Energy as a Service is the Future of Solar Power, https://www.trinasolar.com/us/resources/blog/why-energy-service-future-solar-power, accessed 17/01/2024
-
Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action, European Energy Policy, https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/EN/Artikel/Energy/european-energy-policy.html, accessed 17/01/2024
-
Accilium, Hot Topics in Energy: Top Trends for a Sustainable Future, https://accilium.com/en/introducing-the-hot-topics-in-energy-series-exploring-the-path-to-a-sustainable-future/, accessed 17/01/2024
-
PV Magazine, Mit unseren Solar-as-a-Service Angeboten helfen wir regionalen Solar-Fachbetrieben im Wettbewerb mit den Großen der Branche zu bestehen, https://www.pv-magazine.de/unternehmensmeldungen/mit-unseren-solar-as-a-service-angeboten-helfen-wir-regionalen-solar-fachbetrieben-im-wettbewerb-mit-den-grossen-der-branche-zu-bestehen/, accessed 17/01/2024

