A key part of an electric vehicle (EV) is its battery, which consists of a range of valuable raw materials, including lithium, cobalt, manganese, nickel, and copper. Due to the low availability of these commodities and their environmentally hazardous production methods, recycling of production scrap and end-of-life batteries will be a major factor for the economic and sustainable production of EV batteries. As few end-of-life batteries are currently available for recycling, battery production scrap will be the main source of recyclable EV battery material for the next years.
Current approaches to EV battery recycling reach raw material recovery rates of 90-95%. According to McKinsey, the total supplied volume for EV battery recycling is expected to grow from 50 kilotons in 2020 to 20,500 kilotons in 2040. IDTechEx estimates the global Li-ion battery recycling market of EVs and production scrap to grow from ~100 GWh in 2022 to ~3,000 GWh in 2042 (~35% CAGR).
This enormous growth pattern is caused by the ever-increasing adoption of EVs, recycling technology advancements, supply chain stability pressures to secure scarce raw materials at stable prices, sustainability targets, government incentives, and regulations. Per ton of battery recycling material, McKinsey expects a margin of 13% in 2025, with higher margins possible in the future. Moreover, McKinsey estimates EV battery recycling’s value creation potential to be of USD 95 billion per year by 2040.
OEMs, battery manufacturers, and recycling companies are active in EV battery recycling
These growth expectations attract different types of players to enter the EV battery recycling business. The players can be categorized in OEMs and battery manufacturers on the one side and recycling companies on the other side. A traditional, simple business model for OEMs and battery manufacturers would be to pay fees to recycling companies to transfer the ownership of battery scrap and end-of-life batteries. The recycling company takes over the whole recycling process and either uses recycled materials itself or sells them.
In the following illustration, the KnowledgeAgent Automotive & New Mobility team presents four archetypes of innovative business models for EV battery recycling. These archetypes show which business models can be applied to participate in the growing EV battery recycling market. Moreover, reasons why OEMs and battery manufacturers as well as recyclers are active in the EV battery recycling market are shown. The four archetypes will be outlined in more detail below.
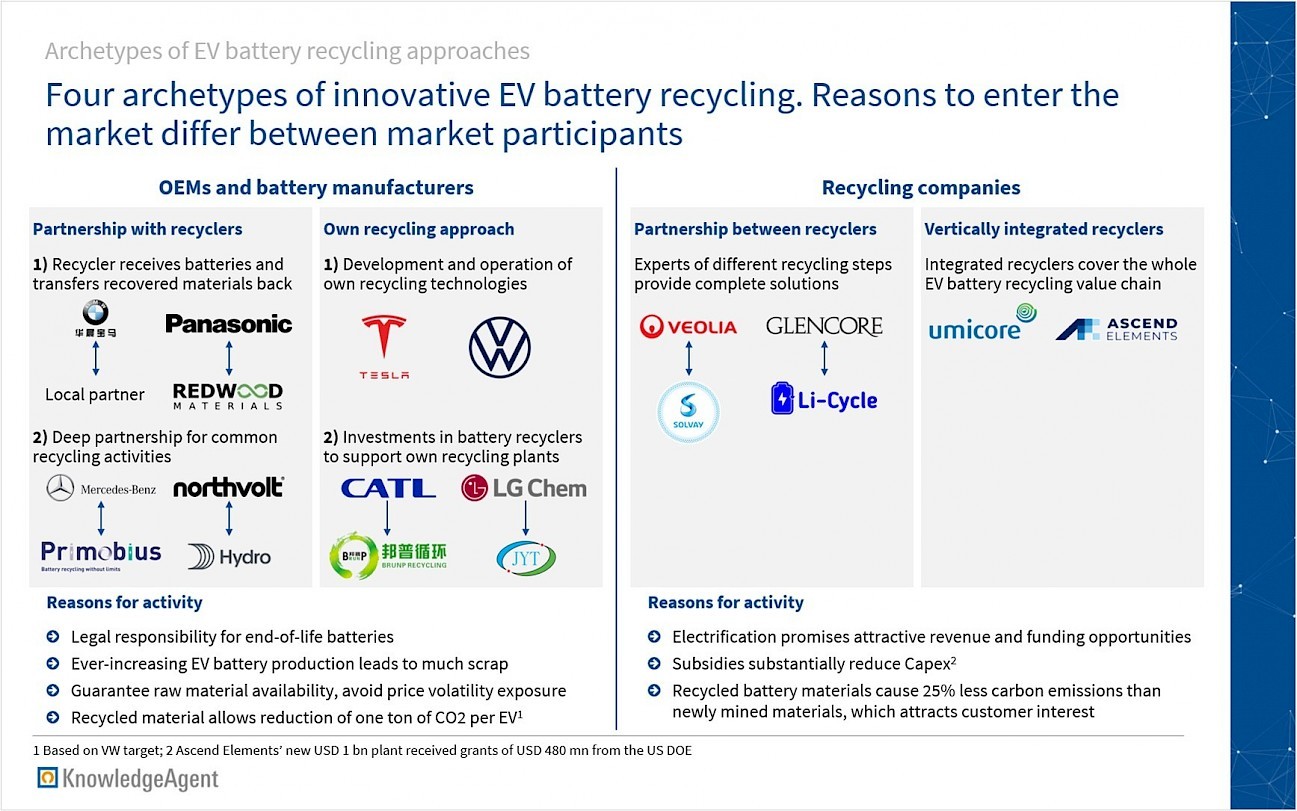
Archetype I: Partnership between OEM / battery manufacturer and a recycling company
One option is a tolling model, used for example by the BMW-Brilliance joint venture in China, in which a recycler receives a fee for recycling, while the OEM keeps the ownership of recycled materials. Similarly, Redwood recycles and extracts materials such as cobalt, nickel and lithium from production scrap of a Panasonic plant. These materials are then supplied back to Panasonic. The tolling model is expected to be the dominant model in the future.
Mercedes-Benz will use another model in its new Kuppenheim, Germany plant. Here, Primobius is Mercedes’ technology partner and will be responsible for recycling directly in the plant.
Battery manufacturer Northvolt and recycler Hydro opened Europe’s largest EV battery recycling plant, called the Hydrovolt joint venture, in 2022. This 50-50 joint venture recycles battery materials and aluminum from Norway’s end-of-life EV batteries.
Archetype II: Own recycling approach of OEM / battery manufacturer
Tesla and VW as pioneering OEMs have developed their own recycling technologies. This approach is used for the recycling of production scrap and end-of-life batteries in own plants in Germany and the US. Both players can recover over 90% of raw battery materials from end-of-life batteries.
Market leading battery producers CATL and LG Chem have made equity investments in battery recyclers to get support for own recycling plants. CATL’s recycling approach mainly relies on Brunp, described as the company’s battery recycling subsidiary, in which CATL holds a 65% stake. LG Chem has invested in Jae Young Tech to establish a battery recycling joint venture in North America. While LG Chem will establish the business model, Jae Young Tech will have the technology lead.
Archetype III: Partnerships between recycling companies
Recyclers that are experts in one EV battery recycling activity partner with specialists that focus on other value chain steps to provide complete recycling solutions. Veolia and Solvay cooperate in this way. First, Veolia uses a chemical extraction process. Then, Solvay applies a hydrometallurgical process to purify precious materials.
Another partnership is the one between Glencore, a major recycler, and Li-Cycle, a specialist in lithium-ion battery resource recovery. The companies plan to build a facility in Italy that produces battery materials from recycled battery content. Li-Cycle’s hydrometallurgical technology will be used, while Glencore adds other recycling experience to the plant.
Archetype IV: Vertically integrated recyclers
Some recyclers have such a high level of vertical integration that they cover the whole EV battery recycling value chain with limited partnerships only. An example is materials technology and recycling corporation Umicore, which covers metals refining, cathode precursor production, and final sales of materials on its own in different plants.
Similarly, US startup Ascend Elements covers pre-processing, material extraction, cathode precursor and active material production, and sales of the material in established and planned facilities.
EV battery recycling is a sustainable business model with strong growth potential
A range of business models allow different types of players to offer innovative solutions for the recycling of EV batteries. As McKinsey estimates that recycled battery materials cause about 25% less carbon emissions than newly mined materials, all these battery recycling models have a strong impact on sustainability. In addition, high growth projections support the further development of the EV battery recycling market.
Are you interested in further insights about EVs or EV battery recycling? Don’t hesitate to contact us!
Sources
-
McKinsey & Company, 13/03/2023, Battery recycling takes the driver’s seat, https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/battery-recycling-takes-the-drivers-seat, accessed 04/08/2023
-
EVBox, 20/01/2023, Are electric car batteries recyclable?, https://blog.evbox.com/are-ev-batteries-recyclable, accessed 04/08/2023
-
IDTechEx, 29/11/2021, Why Are OEMs Investing in Li-ion Battery Recycling?, https://www.idtechex.com/en/research-article/why-are-oems-investing-in-li-ion-battery-recycling/25376, accessed 04/08/2023
-
GEP, 29/05/2023, Battery Recycling: The Next Big Thing in the Global EV Market, https://www.gep.com/blog/mind/why-battery-recycling-is-the-next-big-thing-in-the-global-ev-market, accessed 04/08/2023
-
BMW, 25/02/2022, BMW Group creates closed recycling loop for high-voltage batteries in China, https://www.press.bmwgroup.com/global/article/detail/T0393733EN/bmw-group-creates-closed-recycling-loop-for-high-voltage-batteries-in-china?language=en, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Techcrunch, 15/11/2022, Redwood Materials to supply Panasonic with cathode material in multibillion-dollar deal, https://techcrunch.com/2022/11/15/redwood-materials-to-supply-panasonic-with-cathode-material-in-multi-billion-dollar-deal/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Mercedes-Benz, 03/03/2023, Groundbreaking for battery recycling factory, https://group.mercedes-benz.com/company/news/recycling-factory-kuppenheim.html, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Primobius, 03/03/2023, Mercedes-Benz relies on Primobius technology and lays foundation stone for sustainable battery recycling factory, https://www.primobius.com/news-media/press-releases/detail/mercedes-benz-relies-on-primobius-technology-and-lays-foundation-stone-for-sustainable-battery-recycling-factory, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Hydro, 01/06/2020, Hydro and Northvolt launch joint venture to enable electric vehicle battery recycling in Norway, https://www.hydro.com/de-DE/medien/news/2020/hydro-and-northvolt-launch-joint-venture-to-enable-electric-vehicle-battery-recycling-in-norway/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Northvolt, 15/05/2022, Europe’s largest electric vehicle battery recycling plant begins operations, https://northvolt.com/articles/hydrovolt/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Electrek, 08/09/2021, Tesla claims 92% battery cell material recovery in new recycling process, https://electrek.co/2021/08/09/tesla-battery-cell-material-recovery-new-recycling-process/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Volkswagen, 29/01/2021, Aus alt mach neu – Batterierecycling in Salzgitter, https://www.volkswagen-newsroom.com/de/storys/aus-alt-mach-neu-batterierecycling-in-salzgitter-6782, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Electrive, 09/04/2019, CATL & Brunp Recycling launch joint venture, https://www.electrive.com/2019/09/04/catl-brunp-recycling-launch-joint-venture/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Reuters, 12/10/2021, EV battery maker CATL plans $5-billion China recycling facility, https://www.reuters.com/world/china/ev-battery-maker-catl-plans-5-billion-china-recycling-facility-2021-10-12/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Electrive, 31/01/2023, CATL invests €3.25 billion in recycling plant in China, https://www.electrive.com/2023/01/31/catl-invests-e3-25-billion-in-recycling-plant-in-china/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
LG, 21/12/2022, LG Chem Makes Equity Investments in Battery Recycling Company, Jae Young Tech, https://www.lgcorp.com/media/release/25705, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Solvay, 05/07/2021, Solvay and its partner Veolia set up demo plant for recycling battery metals, https://www.solvay.com/en/press-release/solvay-and-its-partner-veolia-set-demo-plant-recycling-battery-metals, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Glencore, 09/05/2023, Glencore and Li-Cycle announce joint study to develop a European recycling hub, repurposing an existing Glencore metallurgical facility to be the largest source of recycled battery grade lithium as well as recycled nickel and cobalt in Europe, https://www.glencore.com/media-and-insights/news/glencore-and-li-cycle-announce-joint-study-to-develop-a-european-recycling-hub, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Li-Cycle, 21/04/2022, Li-Cycle Completes Commercial Agreements with LG Chem and LG Energy Solution, who have Recognized Li-Cycle as their Preferred Lithium-ion Battery Recycling Partner in North America, https://investors.li-cycle.com/news/news-details/2022/Li-Cycle-Completes-Commercial-Agreements-with-LG-Chem-and-LG-Energy-Solution-who-have-Recognized-Li-Cycle-as-their-Preferred-Lithium-ion-Battery-Recycling-Partner-in-North-America/default.aspx, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Umicore, 21/09/2022, Umicore inaugurates Europe’s first battery materials gigafactory, https://www.umicore.com/en/newsroom/umicore-inaugurates-europes-first-battery-materials-gigafactory/, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Canary Media, 10/04/2023, One of the biggest battery recycling plants in the US is up and running, https://www.canarymedia.com/articles/recycling-renewables/the-biggest-ev-battery-recycling-plant-in-the-us-is-open-for-business, accessed 04/08/2023
-
Industrial Innovation, 10/05/2023, EV Battery Recycling is Glowing Up and Growing Revenues, https://www.industrial-innovation.com/ev-battery-recycling-is-glowing-up-and-growing-revenues/, accessed 04/08/2023