Navigating Commercialization Barriers as CGTs and CAR-T Redefine Treatment Models
Gene therapies have become life-saving treatment modalities, driven by recent regulatory approvals in hard-to-treat diseases and technological advances in genetic engineering. For instance, as of 2025, over 33 gene therapies have been approved globally for clinical use, including genetically modified cell therapies. Notable additions in 2024 included Amtagvi, the first cell-based gene therapy for solid tumors for the treatment of melanoma, and Beqvez for hemophilia B. In Q1 2025, Neurotech’s Encelto was approved for the treatment of macular telangiectasia type 2, marking another step forward in ocular gene therapy. Recent approvals in Q2 2025, notably include FDA approval for Zevaskyn (pz-cel), the first topical gene therapy targeting Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and China’s approval of its first gene therapy for hemophilia B, BBM-H901.
More than 2,100 gene therapies are currently in development, with approximately 50% representing chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies. These therapies involve patient-derived genetically modified T-cells designed to target and destroy cancer cells, including immunoevasive tumors. CAR-Ts have demonstrated their ability to eradicate advanced leukemias and lymphomas and induce remission in otherwise terminal cases. In 2024, major CAR-T products generated sales of around USD 4.5 billion, with Yescarta leading in revenue.
Figure 1: Gene Therapy Market Snapshots
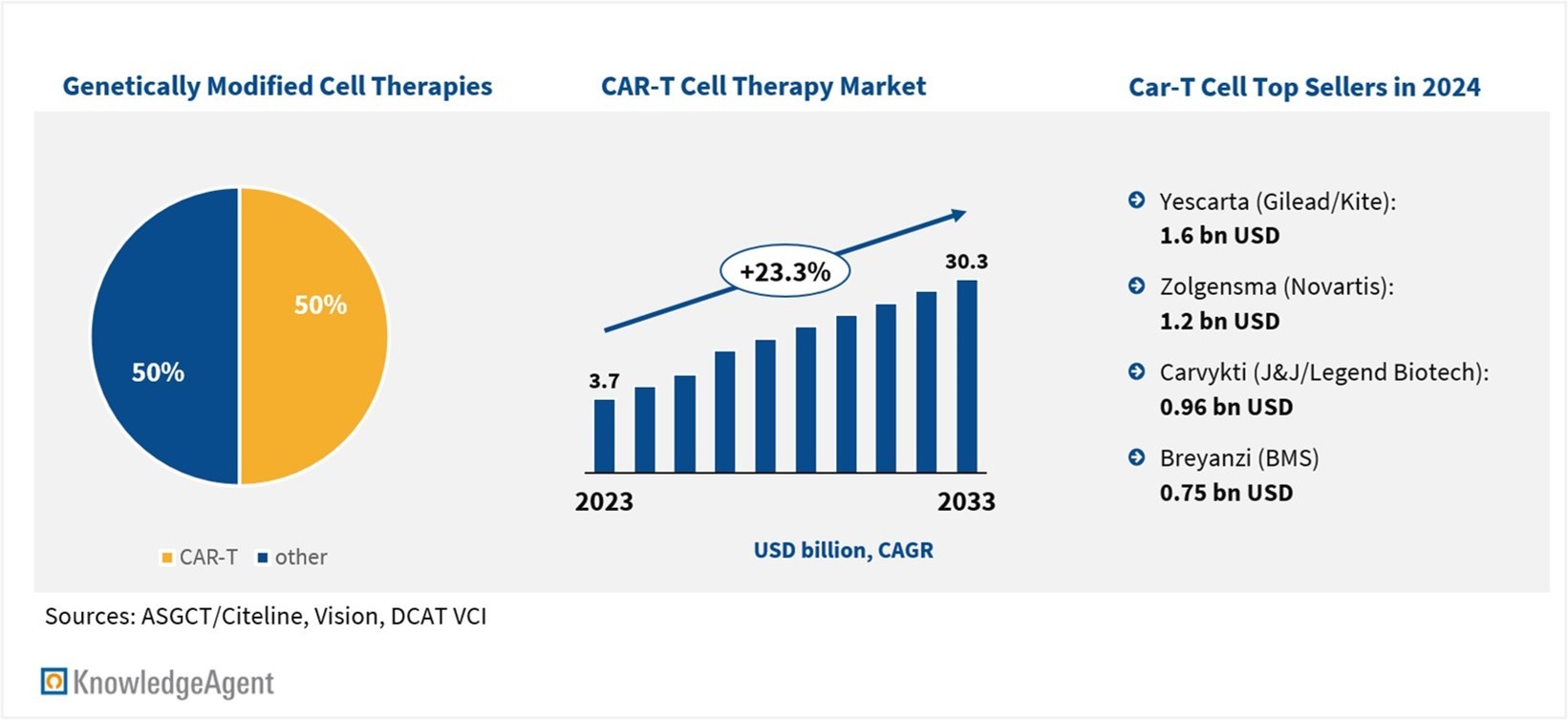
Beyond market projections, CAR-T therapies could generate substantial health systems savings. Consultancy ZS estimates that the reductions in healthcare ecosystem expenditures could add up to more than USD 25 billion from 2024 until 2028. However, realizing this potential will depend on overcoming several obstacles that currently limit broader clinical and commercial adoption. As CAR-T therapies continue to lead the gene therapy space in both development and revenue, understanding and addressing these challenges will be critical. Thus, the next section dives deeper into barriers and levers for unlocking commercial success.
Challenges & Barriers CAR-T: complex manufacturing and logistics
While CAR-Ts are among the most effective cancer therapies available, their development, commercialization, and delivery are hindered by the complexity of manufacturing. The production process involves multiple critical steps (see Figure 2): collecting T-cells from the patient at the care site, transporting the biological material, genetically modifying the cells and manufacturing the final product, conducting quality control, and ultimately administering the personalized treatment back to the patient. Disruptions or delays in any of these phases can have severe consequences for patient outcomes and create complications for providers, manufacturers, and suppliers.
Figure 2: Challenges and Solutions in CAR-T manufacturing
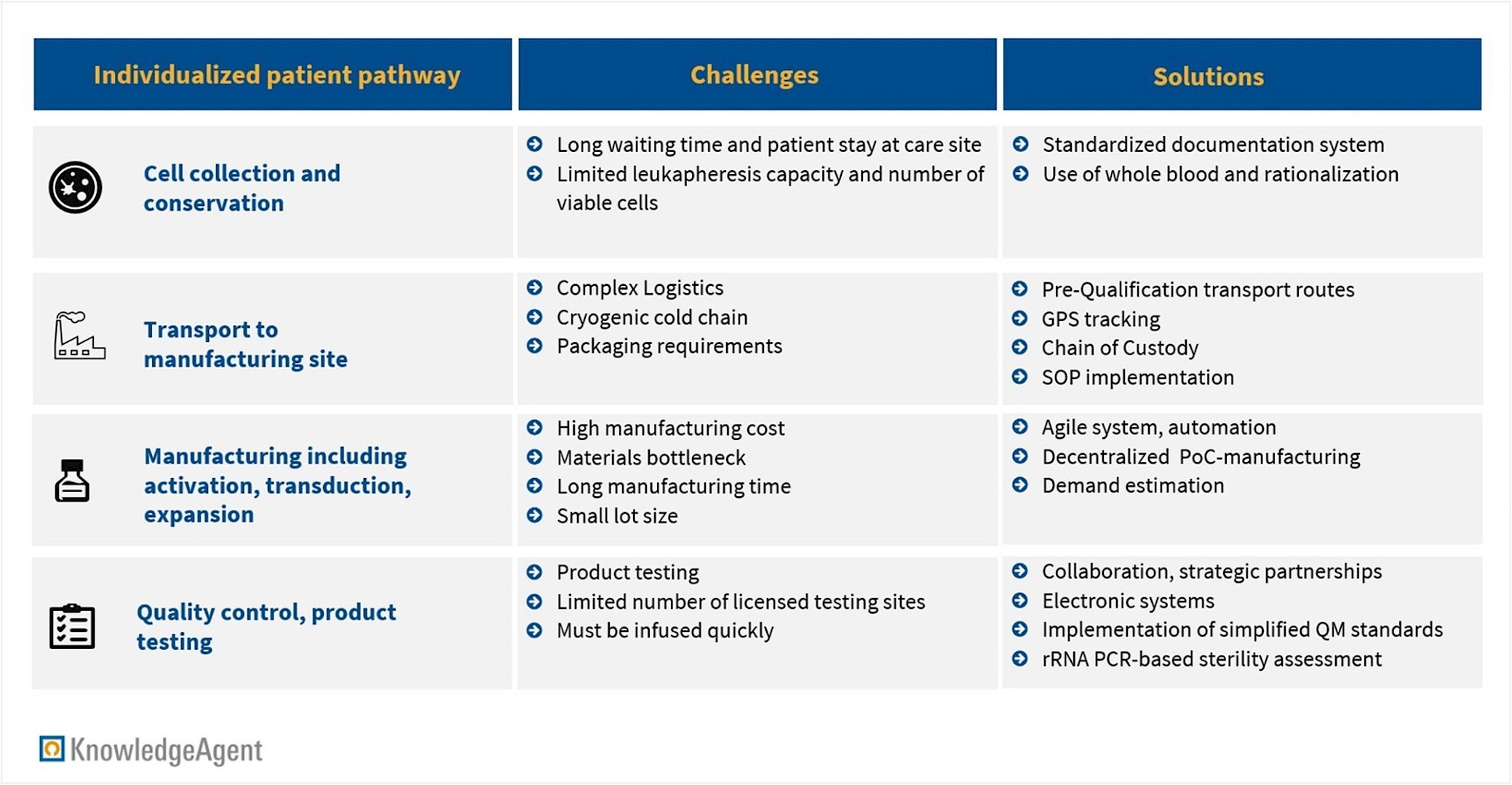
Source: KnowledgeAgent analysis
Industry stakeholders and academia are implementing various strategies to address current challenges in logistics and manufacturing. Key solutions include enhanced logistics infrastructure such as smart containers and real-time cold-chain tracking, demand forecasting to better manage raw material procurement, and pre-qualification of transportation routes to avoid unnecessary delays.
PWC estimates that implementing automation and digitalization in CGT manufacturing could reduce costs by up to 30%. Decentralization is widely recognized as a critical factor for improvement with potential to decrease manufacturing costs to USD 40,000 to 100,000 unit price per batch, (assuming at least 1,000 batches per year, according to an estimate of consulting firm ZS). Another promising approach is point-of-care (PoC) manufacturing, which could lower the vein-to-vein time to just 7 to 14 days. These optimizations are particularly relevant given the current CAR-T therapy price range of USD 55,000 to 450,000 per treatment.
Conclusion
As regulatory approvals expand and technological innovation continues, cell and gene therapies are entering a new phase of increasing clinical and commercial maturity. CAR-T therapies, in particular, are demonstrating value in treating hematologic malignancies and are gaining traction in solid tumors. Yet, to unlock their potential, the field must overcome production and delivery hurdles. Innovations such as automated manufacturing, point-of-care production, and predictive cold-chain logistics are fast becoming differentiators, not optional enhancements. For biotech companies, success now depends as much on execution as on innovation. For investors, spotting firms that treat manufacturing as a strategic asset is key. In an environment shaped by regulatory flux, evolving reimbursement models, and geopolitical pressures, commercial leaders will be those who treat manufacturing and delivery not as support functions, but as core assets that define competitiveness and market access.
How can KnowledgeAgent assist?
To navigate this evolving landscape, companies can make use of targeted, forward-looking market intelligence that goes beyond the lab to capture the broader forces driving success. We address your market and competitive intelligence needs by answering questions such as:
- Who are the main competitors, and how developed are their drug asset pipelines?
- What makes them (un-)successful, and what are their strategic maneuvers in the field?
- What are manufacturing and logistics best practices and which competitors have implemented them?
- What market trends should you be watching to identify new opportunities or threats in the CGT industry?
Sources
-
Abeona Therapeutics, U.S. FDA Approves ZEVASKYN™ (prademagene zamikeracel), the First and Only Cell-Based Gene Therapy for Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB), 04/2025, accessed 23/07/2025
https://investors.abeonatherapeutics.com/press-releases/detail/303/u-s-fda-approves-zevaskyn-prademagene-zamikeracel -
Agliardi et al., Accelerating and optimizing CAR T-cell manufacture to deliver better patient products. Lancet Haematology, 01/2025, accessed 23/07/2025
https://doi.org/10.1016/s2352-3026(24)00273-4 -
American Society of Gene + Cell Therapy (ASGCT), Gene, Cell, & RNA Therapy Landscape Reports, Q1 2025, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.asgct.org/global/documents/asgct-citeline-q1-2025-report.aspx -
American Society of Gene + Cell Therapy (ASGCT), Gene, Cell, & RNA Therapy Landscape Reports, Q4 2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.asgct.org/global/documents/asgct-citeline-q4-2024-report.aspx -
American Society of Gene + Cell Therapy (ASGCT), Gene, Cell, & RNA Therapy Landscape Reports, Q3 2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.asgct.org/global/documents/asgct-citeline-q3-2024-report.aspx -
American Society of Gene + Cell Therapy (ASGCT), Gene, Cell, & RNA Therapy Landscape Reports, Q2 2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.asgct.org/global/documents/asgct-citeline-q2-2024-report.aspx -
American Society of Gene + Cell Therapy (ASGCT), Gene, Cell, & RNA Therapy Landscape Reports, Q1 2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.asgct.org/global/documents/asgct-citeline-q1-2024-report.aspx?_ga=2.41698666.910355479.1719844755-1485106839.171984475 -
Bookimed.com, CAR T-Cell Therapy Cost Effectiveness, 01/2025, accessed 23/07/2025
https://us-uk.bookimed.com/article/car-t-cell-therapy-cost/ -
Dias et al., CAR-T cell manufacturing landscape – Lessons from the past decade and considerations for early clinical development, Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development, 06/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101250 -
DCAT Value Chain Insights (VCI), Cell and Gene Therapies: How is the Market Faring?, 06/2025, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.dcatvci.org/features/cell-and-gene-therapies-where-does-the-market-stand/ -
Fierce Pharma, CAR-T hype faces infrastructure reality check, 01/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/mid-decade-crisis-looms-car-t-cell-therapy -
Hwang et al., Challenges in Global Access to CAR-T cells: an Asian Perspective, Blood Cell Therapy, 02/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://doi.org/10.31547/bct-2023-023 -
PwC, Cell & Gene therapies: How to overcome manufacturing challenges, 12/2023
https://www.pwc.be/en/news-publications/2023/how-to-overcome-manufacturing-challenges.html -
Scherzer Hans-Peter, Cencora World Courier, Supply chain optimization of a CAR-T therapy, 01/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.worldcourier.com/insights/supply-chain-optimization-of-a-car-t-therapy -
Shah et al., Promises and challenges of a decentralized CAR T-cell manufacturing model, Frontiers in Transplantation, 09/2023, accessed 23/07/2025
https://doi.org/10.3389/frtra.2023.1238535 -
Vision Research Reports, Abstract CAR T-cell Therapy Market (By Product: Abecma, Breyanzi; By Disease Indication: Lymphoma, Leukemia, Multiple Myeloma; By End-use) - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, Revenue, Regional Outlook and Forecast 2024-2033, 02/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.visionresearchreports.com/car-t-cell-therapy-market/40008 -
Xinhua, China approves its first gene therapy for rare disease hemophilia B, 04/2025, accessed 23/07/2025
http://english.news.cn/20250411/2c37a74aee124b659c9fa62ed8240940/c.html -
ZS, Decentralized manufacturing: Unlocking CAR-T’s potential, White Paper, 03/2024, accessed 23/07/2025
https://www.zs.com/content/dam/pdfs/Decentralized-manufacturing.pdf

